The Gobi Desert may seem barren, but it hosts remarkable plants of Gobi Desert that thrive against all odds. This article introduces you to the top 10 plants of Gobi Desert and explains their unique adaptations for survival in one of the toughest climates on Earth.
Key Takeaways
- The Gobi Desert is home to extraordinary plant species like the Saxaul tree and saltwort, which have adapted to survive extreme aridity through deep-root systems and specialized photosynthesis methods.
- Goyo, a medicinal plant known for its health benefits, highlights the importance of conservation in the Gobi Desert due to its endangered status caused by habitat destruction and overharvesting.
- Drought-tolerant shrubs and endemic vascular plants play crucial roles in desert stabilization, providing food and habitat for wildlife while necessitating ongoing conservation efforts to maintain biodiversity.
Resilient Flora of the Gobi Desert
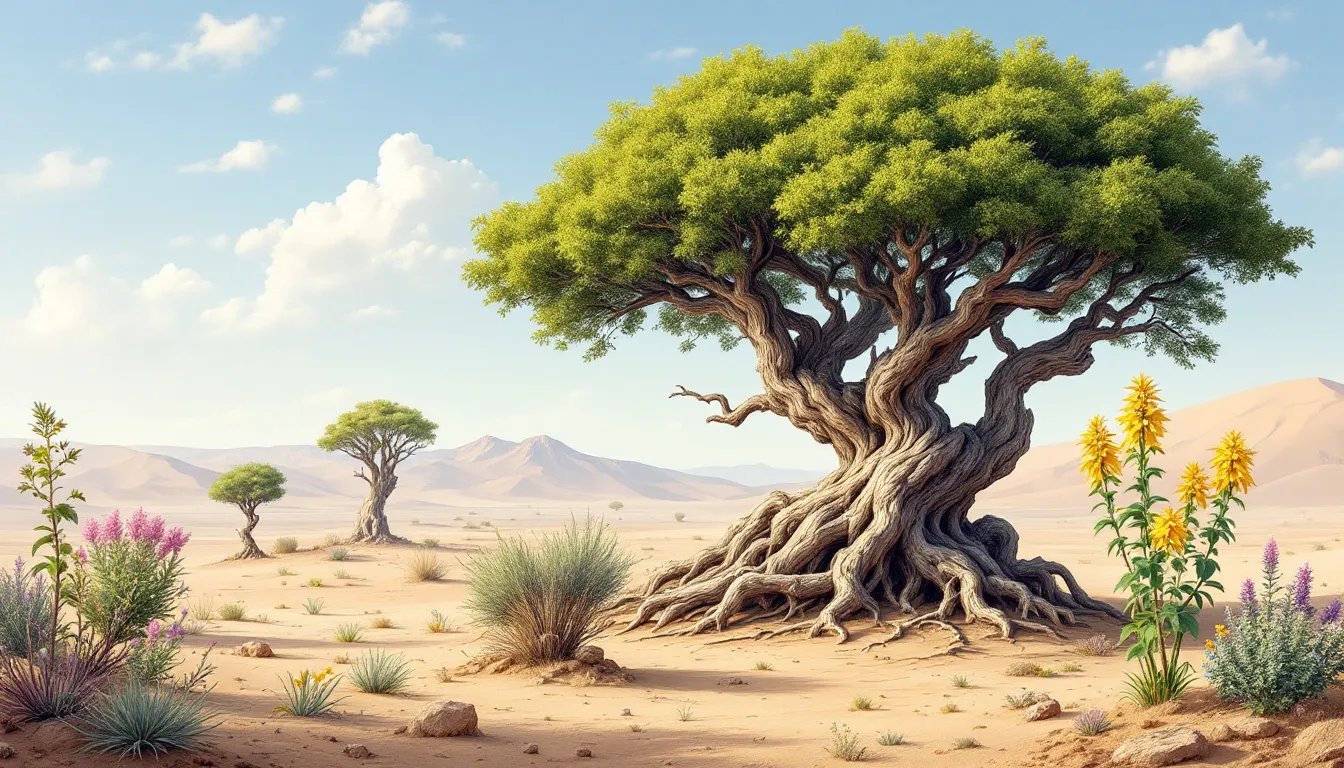

The flora of the Gobi Desert showcases life’s resilience. Despite minimal rainfall, plants have developed extraordinary adaptations.
Species like the Saxaul tree and various shrubs have long roots that reach deep into the ground to access underground water, crucial for survival in an environment with scarce surface water.
Beyond deep roots, some plants of Gobi Desert minimize water loss by taking in carbon dioxide at night and performing photosynthesis during the day, a process known as CAM (Crassulacean Acid Metabolism).
Plants like saltwort, thriving in high-salinity areas, use taproot systems to efficiently absorb moisture.
Though often dwarfed and deformed due to extreme conditions, these plants are vital to the ecosystem, providing food and habitat for animals, including wild camels and nomads.
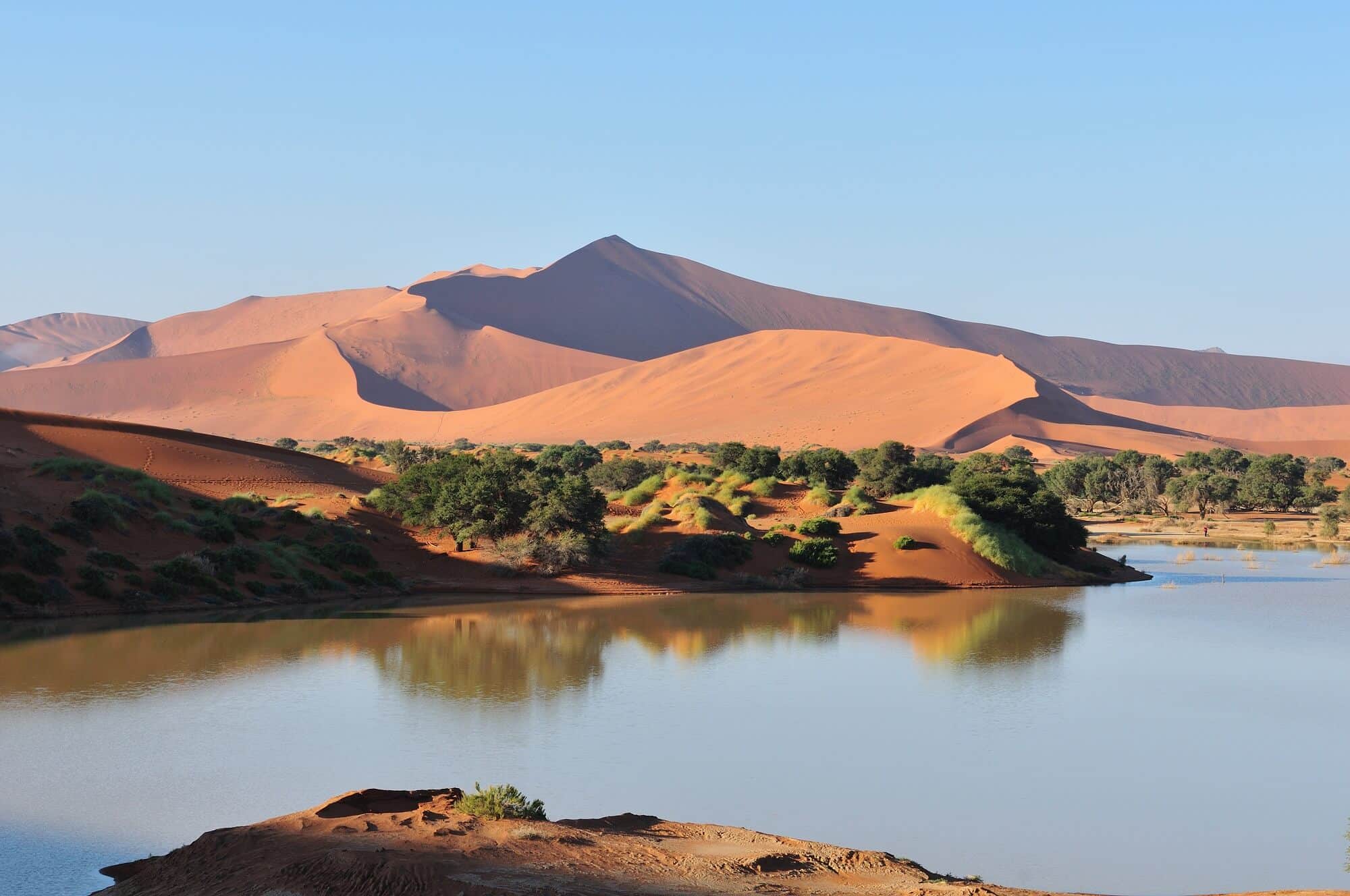
In rare rainy years, the Gobi transforms into a green land with flower steppes, a stark contrast to its usual arid state. The flora here thrives in one of the harshest environments on Earth.
Saxaul Tree: The Desert Stabilizer
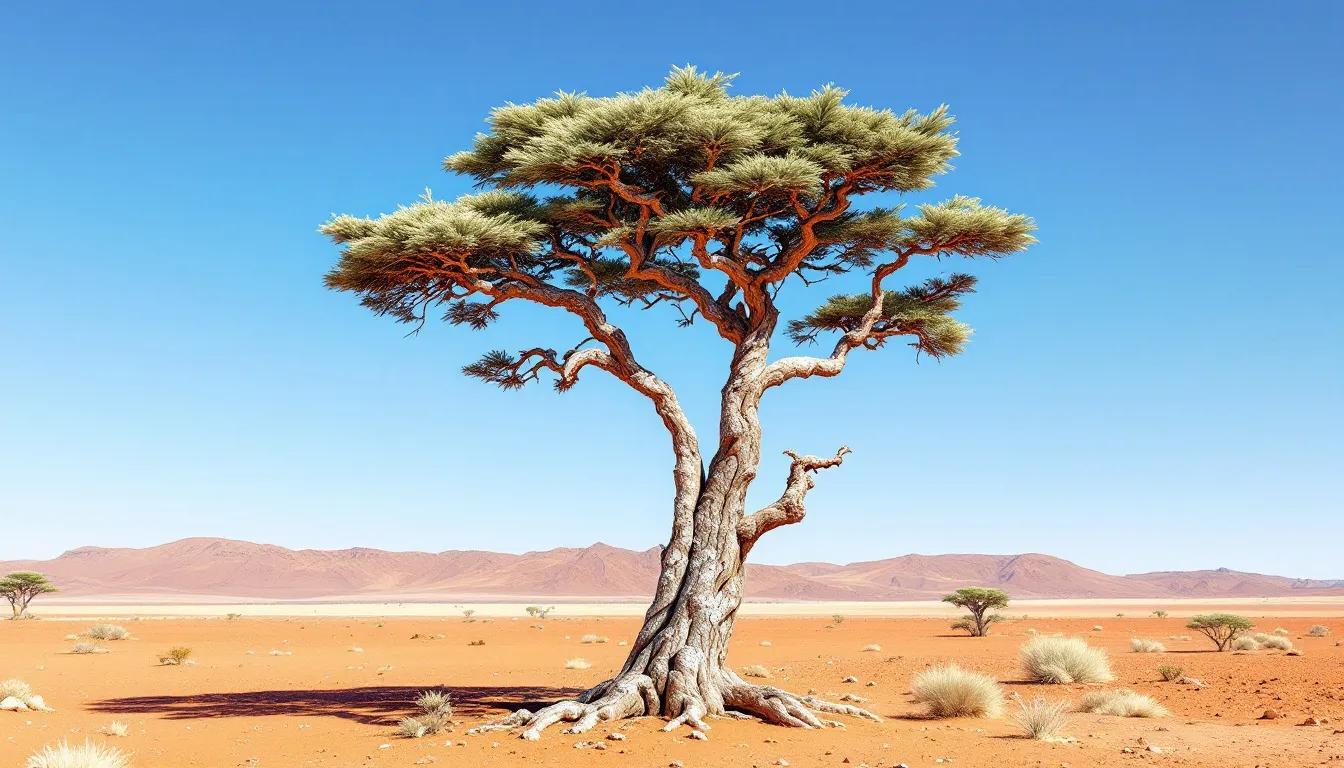

The Saxaul tree epitomizes resilience in the Gobi Desert. Growing up to 12 feet tall, it plays a key role in stabilizing desert soil and preventing erosion. Its extensive root system, reaching depths of up to 30 feet, anchors the tree firmly, combating soil erosion and reducing sand drifts.
A fascinating adaptation of the Saxaul tree is its ability to store water in its spongy bark. This helps it survive Gobi’s arid conditions and provides a vital water source for wildlife and nomads. In a place where water is precious, the Saxaul tree’s moisture retention is remarkable.
Beyond soil stabilization, the Saxaul tree is vital for the ecosystem, offering shade and shelter for animals like wild and Bactrian camels, and serving as a critical resource for local nomads. The Saxaul tree is a stabilizer, provider, and lifeline in arid region of the vast Gobi Desert.
Wild Onion (Allium Mongolicum)
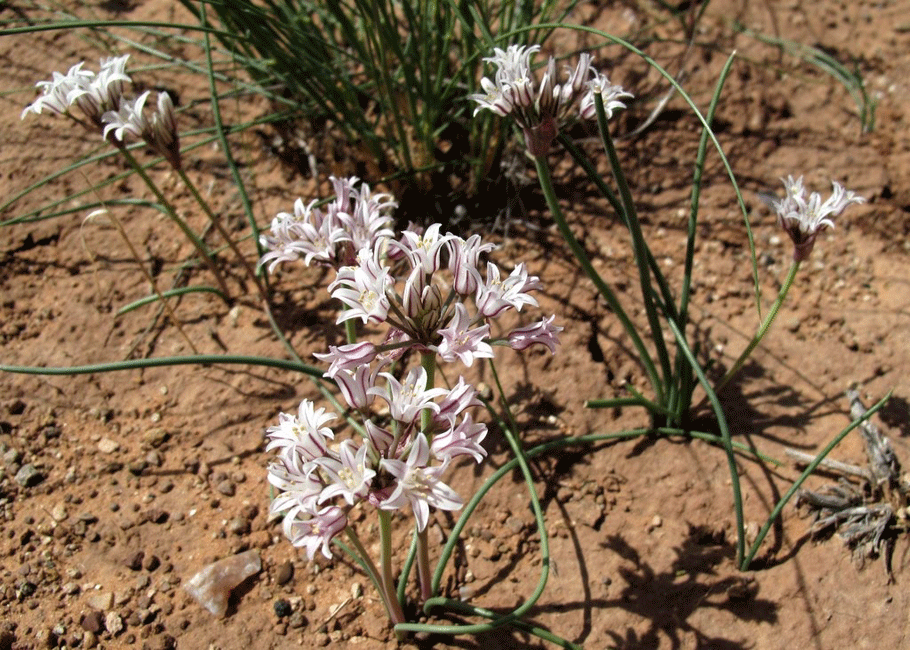
Allium Mongolicum, or wild onion, is another remarkable Mongolian plants of Gobi Desert. This drought-resistant species thrives in the challenging desert steppe and eastern Gobi conditions. Its long roots protect the soil against wind erosion, significantly contributing to soil health.
Beyond its ecological role, the wild onion is a cherished spice and pickled delicacy commonly found in local cuisine.
Goyo: A Medicinal Marvel
Goyo, also known as Allium mongolicum Regel, is famed for its medicinal properties. Traditionally used to treat ailments like high blood pressure, diabetes, and rheumatism, Goyo’s health benefits are well-documented.
Its secondary metabolites, such as flavonoids and phenolics, contribute to its potent antioxidant capabilities, making it valuable for natural medicine.
However, Goyo’s endangered status underscores the need for conservation. Listed in Mongolia’s ‘Red Book,’ its survival is threatened by overharvesting and habitat destruction. Protecting Goyo is about preserving a natural remedy used for generations.
Gobi Berry (Kharmag)
The Gobi berry, or Kharmag, is a nutritional powerhouse in the Gobi Desert. Rich in dietary fibers, vitamin C, and essential minerals like potassium and iron, these berries are vital for both humans and wildlife. Harvesting them requires considerable skill to preserve their quality and taste.
Gobi berries are commonly used to make jams, beverages, and sweet wines, adding a burst of flavor to various culinary delights. Their intricate harvesting process and nutritional benefits make them a treasured resource in the Gobi Desert.
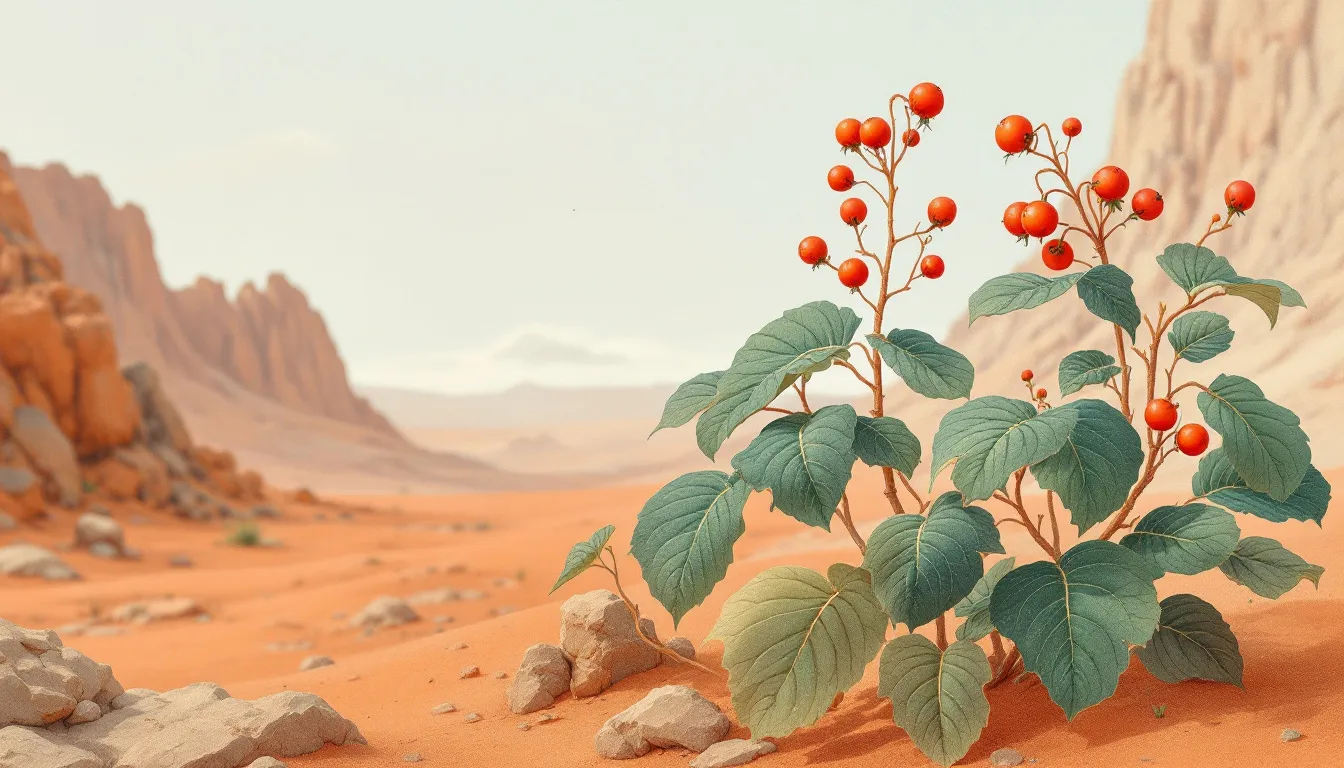

Saltwort: A Summer Bloomer
Saltwort is a resilient plant thriving in the Gobi Desert’s salty and extreme conditions where few others can survive. Its exceptionally long roots efficiently gather moisture from the soil, even in arid environments.
Saltwort blooms from early summer to August winter, propagating its seeds by forming tumbleweeds from detached branches. This unique method ensures the plant’s survival and spread across the harsh Gobi landscape.

Drought-Tolerant Shrubs
Drought-tolerant shrubs, including the saxaul tree and saltwort, are common in the Gobi Desert. These shrubs have evolved to survive extreme arid conditions, with deep root systems accessing water stored below the surface. They are crucial for soil stabilization and preventing desertification.
These shrubs also play a vital role in the ecosystem by providing food and shelter for various wildlife species. Their presence is essential for maintaining the desert environment’s balance, ensuring that life can thrive even in harsh conditions.
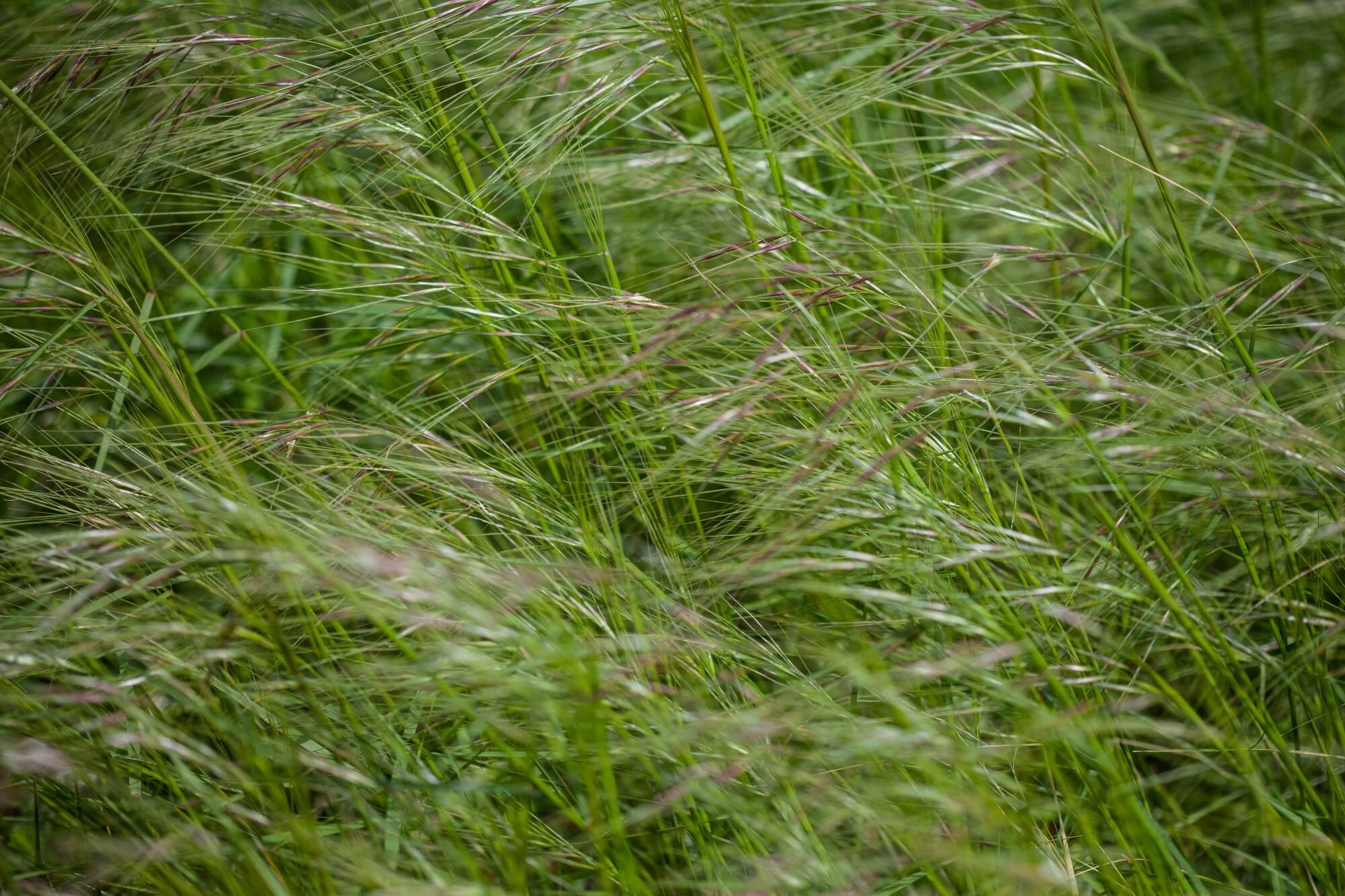
Desert Steppe Grasses

The desert steppe of the Gobi Desert is home to various grasses, including Bridlegrass and Needlegrass. These grasses are vital for the ecosystem, providing forage for wildlife and domestic animals.
Seasonal grazing practices influence the growth and diversity of these species, with rotational grazing methods showing improved outcomes compared to traditional grazing in the eastern gobi desert steppe.
Grazing intensity significantly impacts plant community structure and function in desert steppe ecosystems. Delayed grazing practices can enhance grassland vegetation recovery, aiding in ecosystem stability and productivity.
Endemic Vascular Plants of Gobi desert
The Gobi Desert hosts various endemic vascular plants with specific traits to thrive in semi desert and extreme conditions. These plants, like those with reduced leaf size to minimize water loss, are uniquely adapted to survive in an ecosystem characterized by harsh climates and limited resources.
Conservation efforts in the Gobi Desert focus on protecting these unique plant species from habitat destruction and climate change. Preserving them is crucial for maintaining the region’s biodiversity and ecological balance.
Rare and Relict Species

The central asian gobi desert is home to numerous rare and relict plant species in the western gobi desert region. In the southern and eastern regions, 24 species are classified as ‘sub-endemic’, and 13 are identified as relict. These plants are remnants of a bygone era, offering a glimpse into the desert’s ancient past.
The conservation status of these plants of Gobi desert is concerning, with 10 species considered ‘very rare’ and 4 labeled as ‘rare’. Protecting these species is critical, as many are threatened by habitat destruction and climate change. Preserving these rare and relict species is essential for maintaining the Gobi Desert’s rich biodiversity.
Summary

The Gobi Desert, with its extreme conditions and unique flora, is a testament to the resilience of life. From the Saxaul tree’s soil stabilization to the medicinal marvel of Goyo, each plant plays a vital role in the ecosystem.
Protecting these remarkable plants is essential for preserving the desert’s biodiversity and ecological balance. As we continue to explore and learn about these plants, we gain a deeper appreciation for the ingenuity of nature in one of the world’s most challenging environments.
If you would like to read more about Gobi desert, check the following links
- Gobi desert animals
- Silk Road Gobi Desert: Traversing the Historic Route
- Gobi Desert Mongolia
- Mongolia Snow Leopard Facts – Habitat, Population, and Conservation Efforts
- Snow Leopard Gobi Desert: A Magnificent Beast in a Hostile Landscape
- The Gobi Desert Facts: Top 5 Only Nomads Know in Mongolia
- Gobi Desert Food Web: Plants, Animals, and Ecosystem Explained
Frequently Asked Questions
What are some adaptations of plants of Gobi Desert?
Plants of Gobi Desert have adapted by developing long roots to reach deep water sources, minimizing water loss through nocturnal carbon dioxide intake, and employing taproot systems for efficient moisture absorption. These adaptations are crucial for survival in the harsh desert environment.
How does the Saxaul tree help combat desertification?
The Saxaul tree effectively combats desertification by anchoring the soil with its deep roots, which prevents erosion and mitigates sand drifts. Additionally, its water-storing bark offers essential hydration for wildlife and local nomads.
What are the uses of wild onion (Allium Mongolicum)?
Wild onion (Allium Mongolicum) serves as both a flavorful spice and a pickled delicacy, while also contributing to soil protection against wind erosion. Its versatile applications make it valuable in culinary and ecological contexts.
Why is Goyo considered a medicinal marvel?
Goyo is regarded as a medicinal marvel due to its anti-inflammatory and immune-boosting properties, making it effective in treating ailments such as high blood pressure and diabetes. Its diverse therapeutic benefits enhance its reputation in natural medicine.
What makes Gobi berries (Kharmag) special?
Gobi berries are special due to their high content of dietary fibers, vitamin C, and essential minerals, making them a nutritious addition to various foods such as jams, beverages, and sweet wines. Their versatility enhances both diet and culinary experiences.
Related Tour:
Gobi Desert Tour & Travel 7 days 8 nights
Related Content:
Let us know in the omments below! or join our newsletter today
Share to Public




















