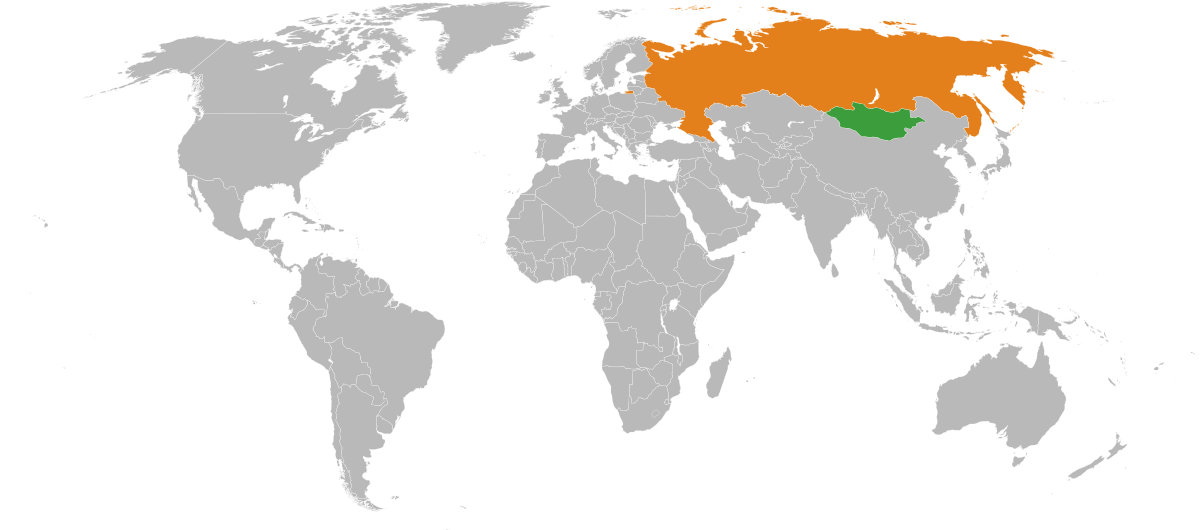
Mongolia-Russia relations encompass a rich history and a multifaceted partnership that includes trade, culture, and humanitarian efforts. In the early 20th century, Outer Mongolia declared independence from China, but was briefly reoccupied by Chinese troops before regaining autonomy.
During this period, Bogd Khan served as the spiritual leader and theocratic ruler, guiding Mongolia through its independence movement. With support from the Soviets and the USSR, a group called the Mongolian People’s Party established the Mongolian People’s Republic in 1924, marking a new era of governance under Soviet influence.
Mongolia played a significant role alongside the Soviets during World War II, particularly in the Battle of Khalkhin Gol.
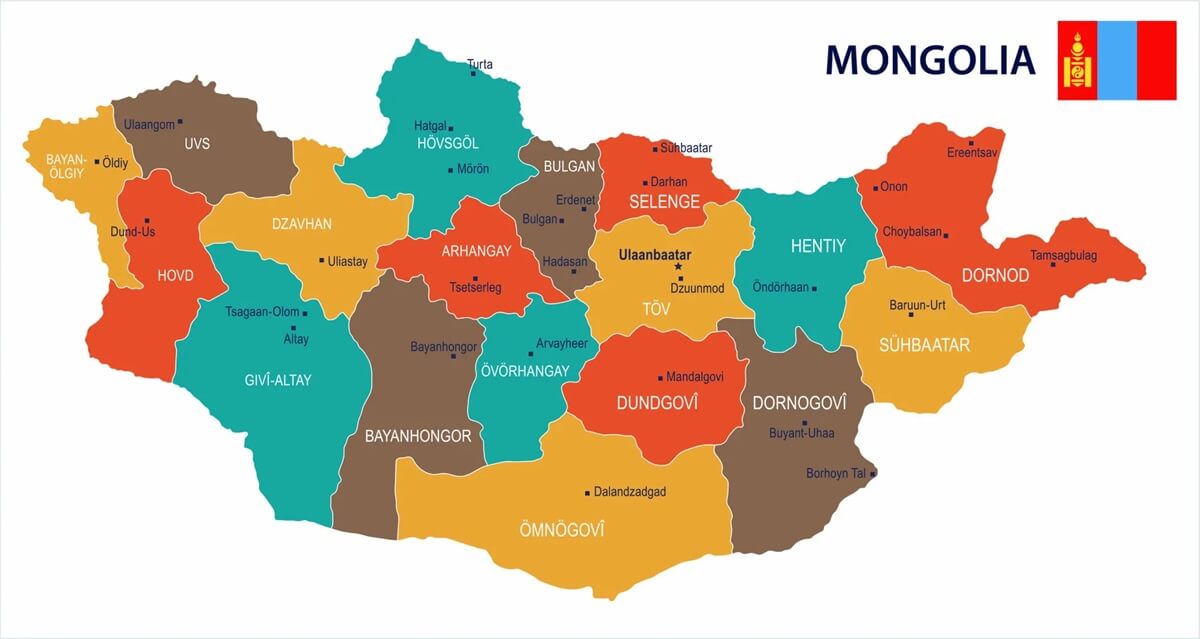
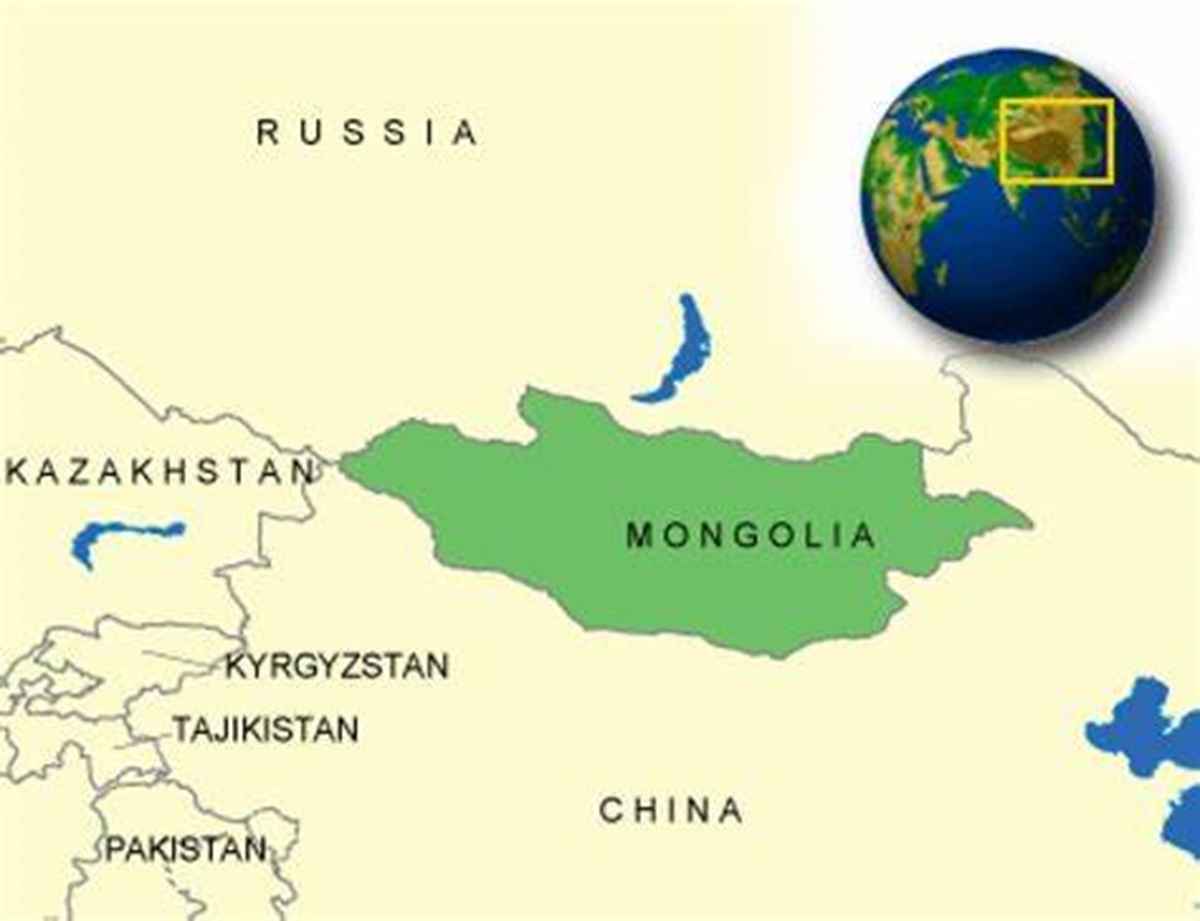
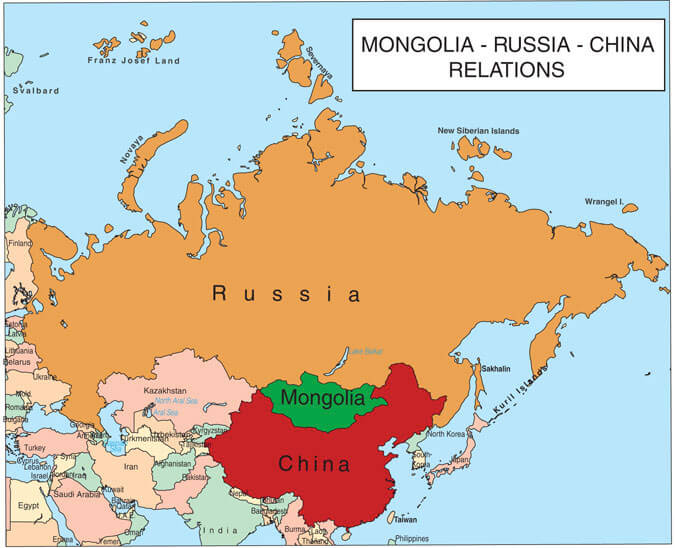
Mongolian territory, strategically located in Central Asia, serves as a key transit route for regional energy and infrastructure projects, highlighting its importance in regional geopolitics. Moscow has long been the center of Russian foreign policy in the region, shaping Mongolia’s political and economic landscape.
Countries signed several agreements, such as the 1986 treaty of peace, friendship, and cooperation, with the Mongolian People’s Party as a key political actor during the communist era.
Mongolia aims to build strategic partnerships with great powers and member states to safeguard its sovereignty and promote stability. This tough balancing act is managed by Mongolian leaders, including the prime minister and Mongolian president, whose policies and outcomes of presidential elections influence Mongolia-Russia relations. Mongolians continue to navigate complex ties with Russia, China, and other great powers.
Mongolia’s membership in international organizations, such as the ICC, brings obligations as one of the member states, especially regarding the ICC warrant for Russian president Vladimir Putin. Recent diplomatic events, including Putin’s visit and the visit to Mongolia by Russian president Vladimir Putin, have tested Mongolia’s neutrality, as the ICC warrant complicates such high-level visits.
The ongoing war in Ukraine has impacted Ukraine Mongolia relations and affected Mongolia’s imports, particularly energy supplies. Russia’s role in Mongolia’s economy remains significant, but international sanctions have created new challenges for trade and investment.
Military and security cooperation continue, with Russian troops participating in joint exercises on Mongolian territory, reflecting a legacy of Soviet and Russian troops’ historical presence. Throughout its history, Mongolia has faced a tough balancing act, with Mongolian leaders and Mongolians striving to maintain independence and stability amid shifting alliances and the influence of great powers.
Key Takeaways:
- Mongolia and Russia have forged enduring ties marked by cooperation and mutual respect despite being neighbors with distinct identities.
- The economic relationship between the two nations is significant, with Russia being Mongolia’s largest trading partner.
- Cultural exchanges enhance the bond between the two countries, reflecting a shared fascination with nomadic heritage.
- Humanitarian projects and conservation efforts highlight a shared commitment to global responsibility and collaboration.
Introduction to the Region
Mongolia, nestled in the heart of East Asia, boasts a storied past that stretches back to the days of the Mongol Empire under the legendary Genghis Khan.
Over the centuries, the region has witnessed dramatic shifts in power, from the collapse of the Mongol Empire to the dominance of the Qing dynasty, and later, the emergence of the Mongolian People’s Republic in 1924—a transformation made possible with the support of Soviet troops.
This rich historical tapestry has shaped modern Mongolia’s identity and its approach to foreign policy.
Strategically positioned between two powerful neighbors, Russia to the north and China to the south, Mongolia’s geopolitical significance cannot be overstated. The country’s location has made it a key player in regional politics and economic cooperation, as it seeks to balance its national interests with the realities of its geographic constraints.
Mongolia russia relations have long been a cornerstone of the country’s foreign policy, with economic ties and bilateral trade playing a vital role in the development of the Mongolian economy.
In recent years, Mongolia has aimed to diversify its economic partnerships, reducing its reliance on Russia and China by strengthening bilateral relations with so-called “third neighbors” such as South Korea, the United States, and Japan.
The Mongolian government has also taken an active role in international organizations, including its membership in the International Criminal Court, and has participated in regional forums like the Ulaanbaatar Dialogue to address pressing issues such as climate change, security, and economic cooperation.
The Russian government, led by President Vladimir Putin, continues to exert significant influence over Mongolia russia relations. The two countries have signed numerous agreements to boost economic cooperation and expand bilateral trade, particularly in sectors critical to the Mongolian economy.
However, the Russian invasion of Ukraine has posed new challenges for Mongolia, especially regarding its dependence on Russian petroleum products and the broader impact on Mongolia’s imports and economic stability.
Despite these complexities, Mongolia remains committed to maintaining stable relations with both Russia and China, while also pursuing its own national interests and independence on the world stage. The country’s foreign policy is shaped by its unique history, strategic geography, and deep-rooted cultural ties with its neighbors.
Recent developments, such as the ICC arrest warrant for Vladimir Putin and Mongolia’s decision to host the Russian president, have drawn international attention and raised important questions about Mongolia’s diplomatic balancing act—particularly in relation to Ukraine, the international community, and its powerful neighbors.
As Mongolia continues to navigate the evolving landscape of Asia, its ability to foster strong relations with Russia and China, while engaging with third neighbors and upholding its sovereignty, will be crucial in shaping the country’s future and ensuring its place as a dynamic and independent actor in the region.
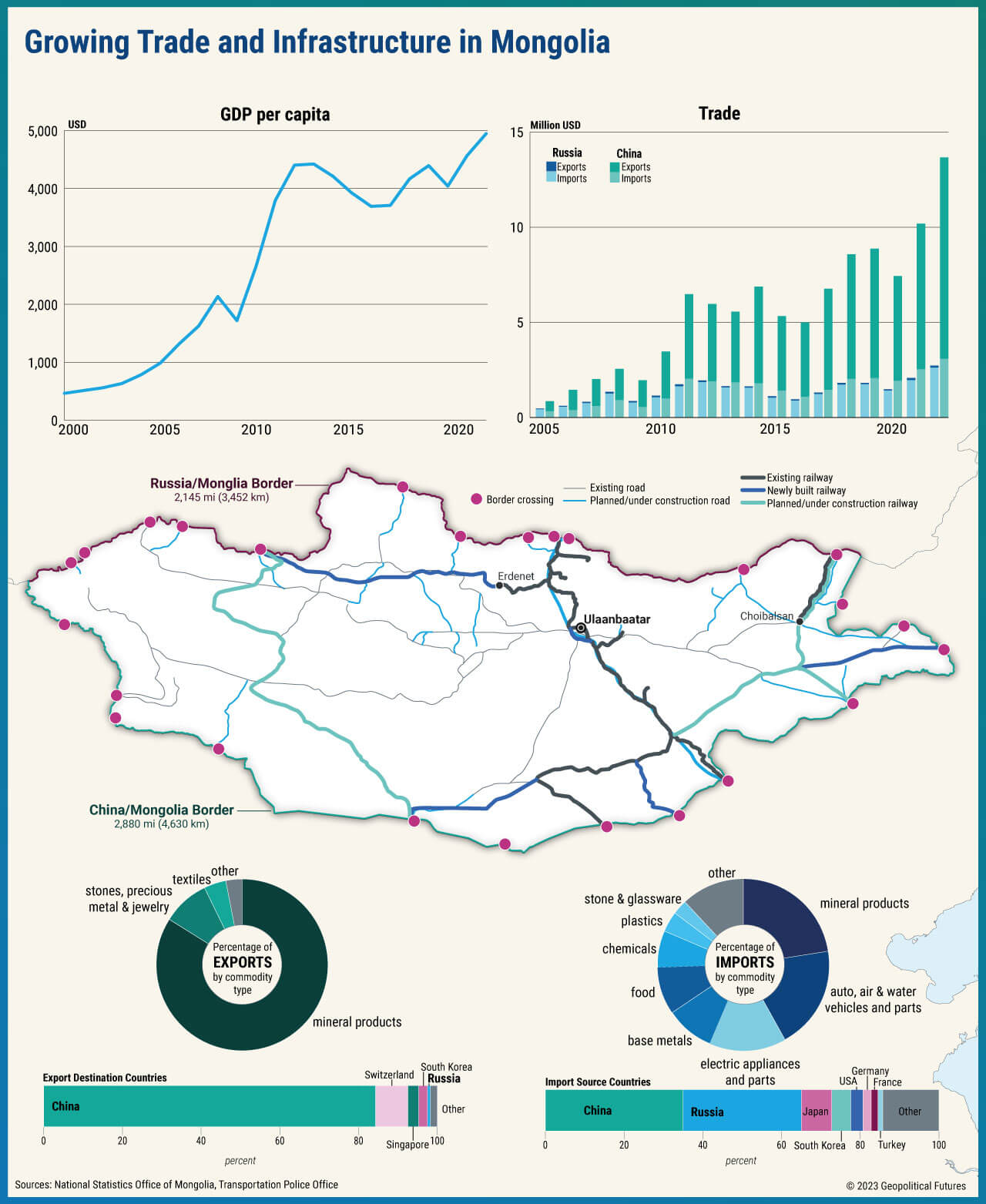
Trade and Economic Relations:
Mongolia and Russia maintain significant trade ties, benefiting from the exchange of goods and services.
Russia is Mongolia’s largest trading partner, and the economic relationship continues to grow.
Mongolia primarily exports minerals like coal and copper to Russia. Mongolia’s imports from Russia include machinery, equipment, and petroleum products, making Mongolia’s imports heavily reliant on Russian energy and industrial goods. Diversifying Mongolia’s imports is important to reduce dependency on a single source and strengthen economic resilience. For travelers interested in local products, here’s a guide to things to buy when visiting Mongolia.
Joint ventures and bilateral agreements bolstered economic collaboration, contributing to both nations’ development and prosperity.
Cultural Relations:
Cultural exchanges play a vital role in enhancing the bond between Mongolia and Russia.
Both countries have a profound appreciation for each other’s traditions and share a fascination with their nomadic heritage.
Russian influence on Mongolian culture is evident in language, literature, and the arts.
Likewise, Mongolian cultural elements like throat singing and traditional attire captivate Russian audiences, fostering cross-cultural understanding.
Festivals, exhibitions, and academic programs serve as platforms for cultural interaction, strengthening these two nations’ ties.
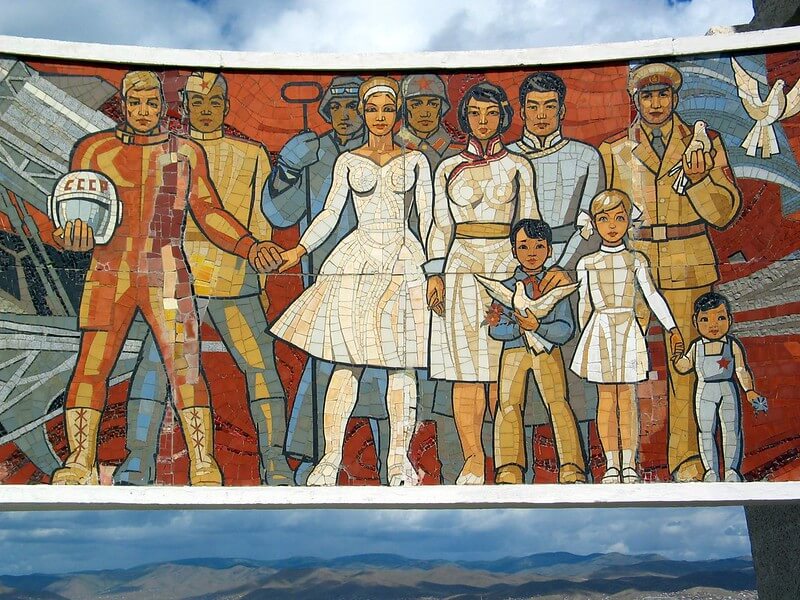



Humanitarian Relations:
Humanitarian cooperation underscores the compassionate aspect of Mongolia-Russia relations. Both countries collaborate on numerous projects aimed at addressing common challenges and supporting vulnerable populations.
This cooperation extends to healthcare, education, and disaster relief. Mongolia and Russia share a commitment to conserving their natural landscapes and biodiversity, working together on conservation initiatives.
These joint endeavors benefit citizens of both nations and reflect a shared sense of responsibility towards the global community.
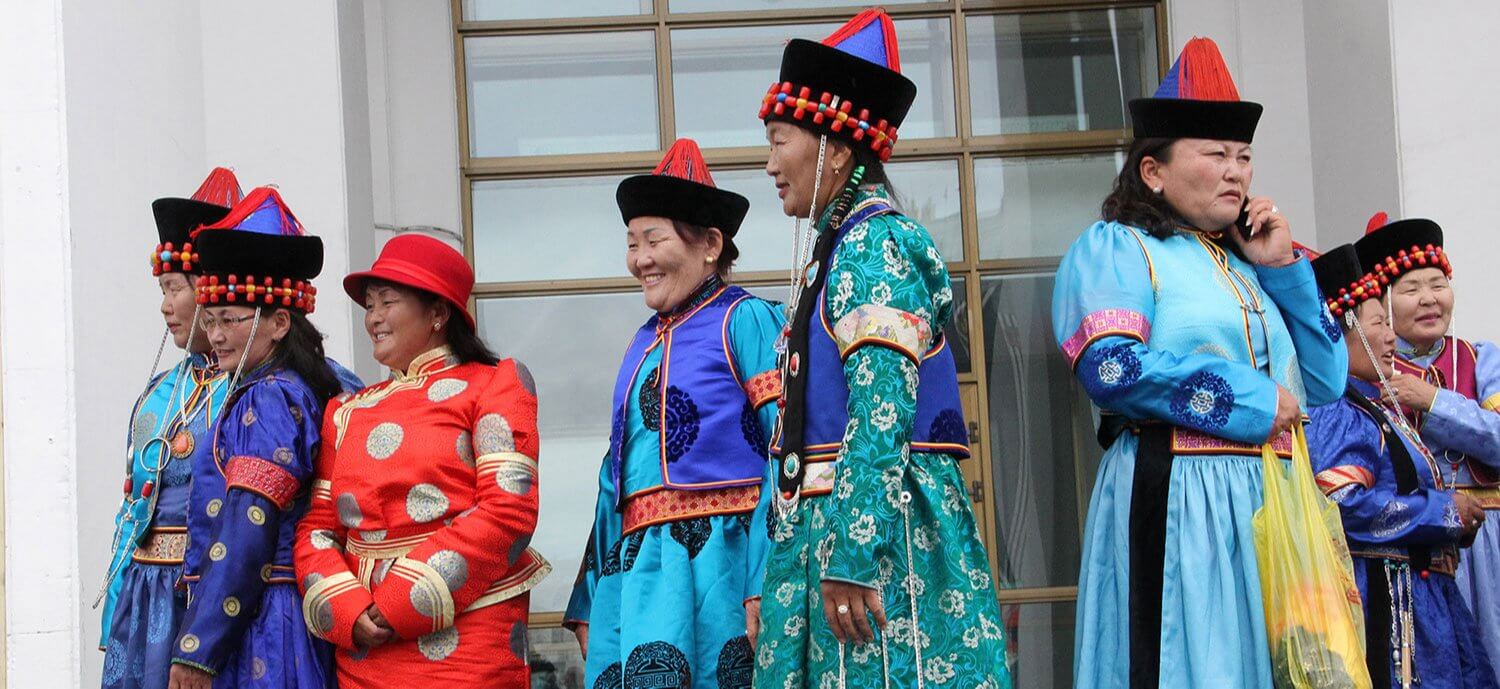

- Ulaanbaatar, the capital of Mongolia, and Ulan-Ude, the capital of the Russian Republic of Buryatia, are sister cities, further strengthening people-to-people connections.
- The Trans-Mongolian Railway, a vital transportation artery linking Russia and Mongolia, facilitates the movement of goods and passengers, promoting economic integration and regional connectivity.
Interesting Facts:
- The historical ties between Mongolia and Russia trace back to the Mongol Empire, which, at its peak in the 13th century, encompassed territories of present-day Mongolia and parts of Russia.
- During world war ii, Mongolia fought alongside the Soviets in the Battle of Khalkhin Gol, a decisive victory that strengthened Mongolia-Russia relations and is commemorated as a significant historical event.
- Mongolia was the second country, after Russia, to recognize the independence of the Russian Federation in December 1991, following the dissolution of the Soviet Union.
- The Treaty of Friendship and Cooperation signed in 1993 serves as the cornerstone of modern Mongolia-Russia relations, fostering political dialogue and partnership in various fields.